What is Bleaching Plant of Vegetable Oil?
The vegetable oil bleaching process is a crucial step in refining edible oils to remove impurities and improve their color, flavor, and shelf life.
The vegetable oil bleaching process begins with pre-treatment of the crude oil, which includes degumming and neutralization. Degumming removes phospholipids, while neutralization eliminates free fatty acids. Once these preliminary steps are complete, the oil is ready for the bleaching stage.
While the process may seem simple, the parameters under which it is conducted are critical. Moisture levels, temperature, contact time and vacuum are just a few of the parameters that affect the process.
efining process.
There are 3 processes via which bleaching can be executed:
1) Mixing Chemical
2) Bleaching
3) Filtration
Process of Bleaching
In the bleaching plant, the oil is mixed with bleaching earth or activated carbon, which are adsorbent materials used to attract and bind impurities. These impurities can include pigments like chlorophyll and carotenoids, as well as traces of metals and oxidation products that affect the oil’s quality.
The process involves heating the oil to a specific temperature, usually between 85°C to 110°C (185°F to 230°F), to enhance the efficiency of the adsorbents. The oil-adsorbent mixture is then agitated to ensure thorough contact between the oil and the adsorbents. This mixture is typically processed under vacuum to prevent oxidation and degradation of the oil.
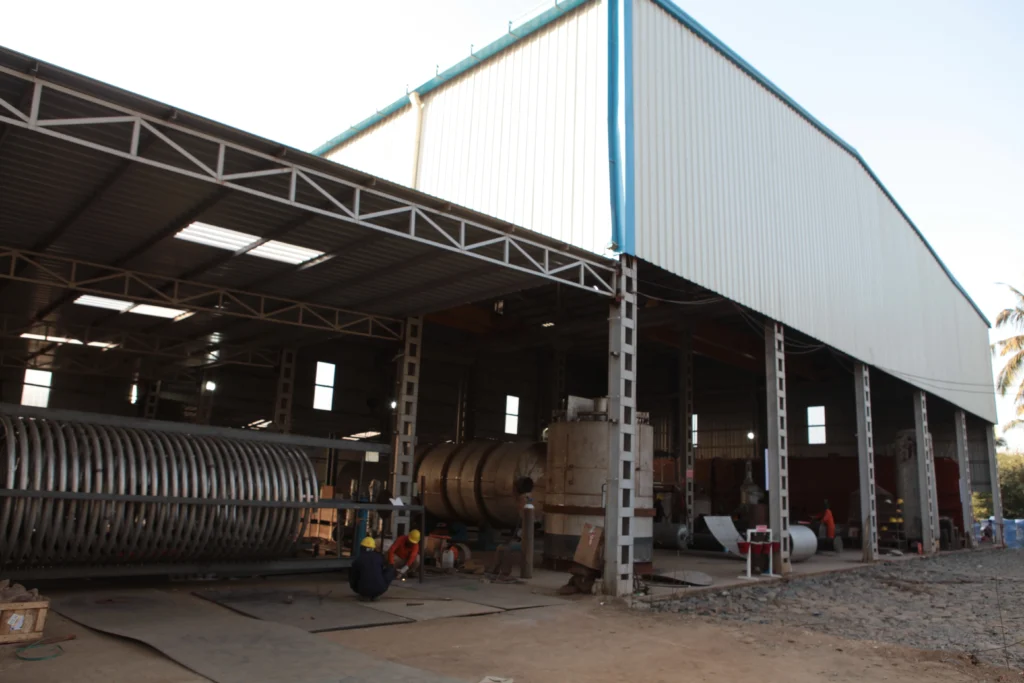

After sufficient contact time, which can vary depending on the type of oil and the extent of impurities, the oil is filtered to separate the spent adsorbents from the bleached oil. The filtration process is critical, as it ensures that no adsorbent residues remain in the final product.
The clarified oil, now free of unwanted colorants and contaminants, is then subjected to further refining steps, such as deodorization, where any remaining odors and volatile compounds are removed. This results in a high-quality, stable, and visually appealing vegetable oil suitable for consumption.
The vegetable oil bleaching process within a bleaching plant is a meticulously controlled operation designed to purify and enhance the quality of edible oils. By effectively removing impurities and improving the oil’s properties, this process plays an essential role in the production of refined vegetable oils.
Advantages of Bleaching Process provided by Muez Hest
- Effective Removal of Color Pigments
- Improved Color Quality
- Enhanced Oil Purity
- Optimized Bleaching Efficiency
- Reduced Bleaching Clay Usage
- Adaptability to Various Oil Types
- Reduction of Process Time
- Enhanced Safety and Control
- Reduced Impact on Deodorizing
- Minimized Oil Waste
Get A Quote to discuss
your manufacturing requirements
Global Installation
Global Installation
Strategies to ensure proactive domination. At the end of the day,User generated content in real-time will have multiple touchpoints for offshoring.
-
0
Project completed
-
0
Satisfied client
-
0
Year of experience
-
0
Qualified specialist
Our Clients
We worked with royal clients























our blogs
Recent News & Articles
March 15, 2025
MuezHest Sponsoring FOIC 2025 in Mumbai
October 20, 2024
Highlights from SOPA Soyconclave 2024
Read More
Bleaching Plant Manufacturers in India & Global – Muez Hest
At Muez Hest, we are one of the leading bleaching plant manufacturers in India, delivering advanced and high-efficiency solutions for the edible oil, oleochemicals and specialty chemical industries. Our bleaching systems are engineered to remove impurities, color bodies and oxidation products, ensuring cleaner, brighter and high-purity outputs.
With years of expertise, we offer fully customized bleaching plant designs that meet global safety and quality standards. Our bleaching units are built for energy-efficient performance, consistent quality and long-term reliability helping businesses achieve superior product clarity and stability.
Whether you require a stand-alone bleaching plant setup, pre-bleaching systems, filtration components or a complete refining line, Muez Hest provides end-to-end solutions from engineering to installation and commissioning.
What Is The Bleaching Process & Why It Matters
The bleaching process is a vital step in refining oils, fats and specialty raw materials. It involves adsorbing and removing pigments, soaps, trace metals and impurities using activated bleaching earth or other adsorbents.
A well-designed bleaching plant setup ensures:
- - Improved oil clarity and color
- - Removal of oxidation catalysts
- - Better stability and shelf life
- - Consistent product performance
- - Reduced contamination and wastage
As trusted bleaching plant manufacturers, Muez Hest designs systems that provide precise temperature control, optimized mixing and effective filtration to ensure the highest purity. Our bleaching solutions support industries like edible oil refining, cosmetics, oleochemicals, nutraceuticals and specialty chemicals.
The accuracy and efficiency of the bleaching stage directly impact the quality of the final product. That’s why industries worldwide trust Muez Hest for modern, safe and high-performance bleaching plant solutions.
Top Bleaching Plant Process
At Muez Hest, a trusted name among leading bleaching plant manufacturers in India and across global markets, we design each bleaching system to ensure superior oil purification, maximum efficiency and consistent quality. The bleaching process begins with the careful selection and pre-treatment of oils or fats, where impurities, pigments, trace metals and oxidation components are reduced for further processing.
Using advanced bleaching reactors, precise temperature control and high-performance adsorbents such as bleaching earth or activated carbon, our bleaching plant effectively removes colour bodies, improves clarity and enhances product stability. Every stage from slurry preparation to bleaching, filtration and final polishing is monitored under strict quality parameters to maintain purity and uniformity.
Our fully engineered bleaching plant setup includes automated systems, optimized energy consumption and advanced filtration units that ensure minimal oil loss and maximum adsorption efficiency. The process is designed to meet both domestic and international refinery standards, guaranteeing high-quality output for edible oils, oleochemicals and specialty products.
As one of the leading bleaching plant manufacturers, Muez Hest focuses on sustainable operation, low maintenance and long-term reliability. Our state-of-the-art bleaching systems help industries achieve consistent colour reduction, improved shelf life and premium-quality refined oils while supporting global demand for clean, safe and high-performance products.
Why Choose Muez Hest as Your Global Bleaching Plant Partner
As one of the leading bleaching plant manufacturers in India and global markets, Muez Hest offers complete turnkey bleaching solutions that ensure efficiency, safety and long-lasting performance.
Complete Turnkey Bleaching Plant Setup
From feasibility study to engineering, manufacturing, installation and operator training, we provide full-scale support to deliver a seamless bleaching plant setup tailored to your capacity and process requirements.
Global Experience, Local Expertise
With clients across industries worldwide, we understand global quality norms and regional market needs, enabling us to deliver high-performance and compliant bleaching plant solutions.
High Purity & Consistent Results
Our plants are equipped with precision temperature control, optimized earth dosing and high-efficiency filtration to ensure consistent color reduction and superior purity.
Customized For Diverse Industries
We build bleaching plants for edible oils, oleochemicals, pharmaceutical intermediates, specialty chemicals and cosmetic applications all tailored to the client's specifications.
Safe, Sustainable & Energy Efficient
We design every bleaching plant setup with a focus on energy savings, minimal earth consumption, low emissions and maximum safety during operation.
Benefits Of Partering With Muez Hest For Bleaching Solutions
Working with Muez Hest, a trusted name among leading bleaching plant manufacturers, offers many advantages for businesses that want to set up or upgrade their oil refining and purification systems.
- - Fast setup with turnkey solutions – We provide complete support for your bleaching plant setup, including design, engineering, installation and commissioning. This helps you start production faster with a smooth and hassle-free process.
- - Safe and reliable bleaching plant design – Our bleaching plant systems are created to ensure safe, stable and efficient removal of colour pigments, impurities and unwanted materials from oils and fats. This reduces operational risks and improves long-term performance.
- - Consistent product quality – With precise temperature control, advanced bleaching earth handling and high-efficiency filtration, we help industries achieve uniform, high-quality output every time.
- - Lower operating costs – Our energy-efficient designs, smart automation and optimized process flow help reduce bleaching earth consumption, oil loss and overall production costs.
- -Support for both domestic and global markets – Muez Hest designs bleaching plant systems that meet Indian and international refinery standards. This allows manufacturers to supply purified, premium-grade oils to both local and global markets.
Muez Hest’s expertise ensures smooth, safe and high-performance bleaching operations, making us a reliable partner for industries looking for long-term, scalable and cost-efficient bleaching solutions.
Global Bleaching Plant Setup Steps & Muez Hest's Proven Approach
We follow a structured and professional methodology to deliver high-efficiency bleaching plants worldwide:
- Consultation & Requirement Analysis: We understand your product type, desired color specifications, production goals, capacity and budget to design the right bleaching plant setup.
-
Design & Engineering: Our experts prepare P&IDs, layout plans, process flow diagrams and define key parameters to ensure safe, optimized and consistent bleaching operations.
- Manufacturing & Component Sourcing: Reactors, filters, dosing systems, vacuum units and control panels are either manufactured in-house or sourced from trusted global partners.
-
Installation & Commissioning: We handle complete installation, alignment, vacuum testing, filtration checks and performance tests to ensure your bleaching plant runs smoothly from day one.
- Training & After-Sales Support: We provide operator training, maintenance support and periodic audits to ensure long-term plant performance and efficiency.
Your Trusted Bleaching Plant Setup Partner
Partner with Muez Hest, a globally trusted name in bleaching plant manufacturing and achieve superior product clarity, stability and overall refining efficiency. Whether you are building a new unit or upgrading an existing system, our advanced technology, high-quality engineering and turnkey support guarantee reliable performance.
Our bleaching solutions ensure better color reduction, improved product stability and high purity across applications like edible oils, oleochemicals, cosmetics and specialty chemicals.
Contact Muez Hest today to set up a world-class bleaching plant that enhances your production quality and supports sustainable, long-term growth.
faq
Frequently Asked Questions
Discover some of the most asked questions regarding Bleaching plant.
What is a bleaching plant?
A bleaching plant is a facility where edible oils and fats are treated with bleaching agents to remove color pigments, impurities, and other unwanted substances, enhancing the oil’s appearance and quality.
Why is bleaching necessary in oil processing?
Bleaching is necessary to remove color pigments, such as carotenoids and chlorophyll, as well as trace metals and other impurities that can affect the oil’s color, flavor, and stability.
What are the main types of bleaching agents used?
Common bleaching agents include activated clay (bleaching earth), activated carbon, and synthetic adsorbents. Each agent has specific properties suited for different types of oils.
How does the bleaching process work?
The process involves mixing the crude oil with a bleaching agent, which adsorbs the color pigments and impurities. The oil is then filtered to remove the spent bleaching agent and contaminants.
What are the benefits of the bleaching process?
Benefits include improved oil color, enhanced visual appeal, reduced off-flavors, and increased stability of the final product.
What environmental considerations are associated with a bleaching plant?
Environmental considerations include managing waste generated from spent bleaching agents, ensuring proper disposal or recycling, and minimizing water and energy use.
How does the bleaching plant integrate with the overall oil refining process?
Bleaching is a key step following degumming and alkali refining, and it precedes deodorization. It prepares the oil by improving its color and removing impurities before further refining.
Go To Top



