Pretreatment: Batch / Continuous Type
Optimizing Feedstock, Enhancing Product Quality
Optimizing Feedstock, Enhancing Product Quality
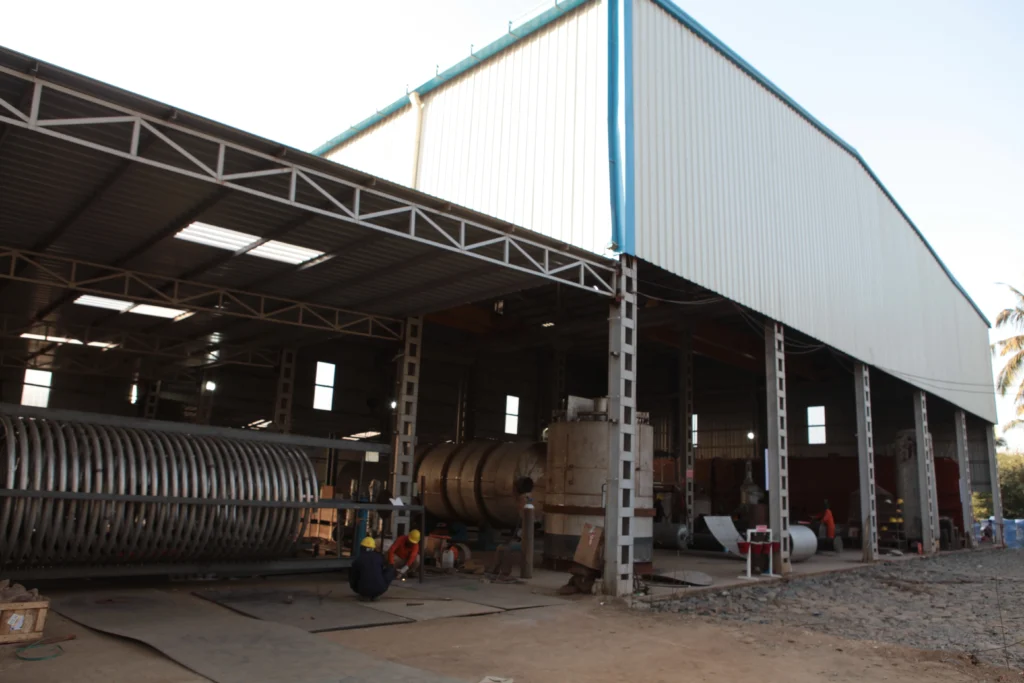
Pretreatment in oleochemical processes involves preparing natural oils and fats by removing impurities before further processing. This step is crucial for producing high-quality oleochemicals. The feedstock is treated with activated bleaching earth, commonly known as diatomaceous earth, at a concentration ranging from 0.1% to 2%. This process helps eliminate byproducts such as protein degeneration, soaps, ash, and colorants.
Applications: Pretreatment is used for various feedstocks, including recovered and high-color oil, acid oil, used cooking oil, and raw tallow. It effectively reduces sludge and waste material, improving the quality of the final oleochemical products.
Pretreatment is a crucial step in oleochemical production, involving the purification of natural oils and fats by removing impurities like proteins, soaps, ash, and pigments. This is achieved by treating the feedstock—such as recovered oils, acid oil, used cooking oil, or raw tallow—with 0.1% to 2% activated bleaching earth (diatomaceous earth). This process ensures high-quality oleochemicals and reduces waste. The spent bleaching earth, containing impurities, is removed as sludge, while regular maintenance of the filtration system ensures consistent product quality.

Strategies to ensure proactive domination. At the end of the day,User generated content in real-time will have multiple touchpoints for offshoring.























March 15, 2025
October 20, 2024
Discover some of the most asked questions regarding Pretreatment Batch Continuous.
Feedstocks such as recovered and high-color oils, acid oil, used cooking oil, and raw tallow can be effectively pretreated with bleaching earth.
Bleaching earth, also known as diatomaceous earth, is used to remove impurities such as proteins, soaps, ash, and coloring materials from the feedstock. This step is crucial for producing high-quality oleochemicals.
The optimal amount of bleaching earth ranges from 0.1% to 2% of the feedstock weight. The exact amount depends on the level of impurities and the desired quality of the final product.
Proper pretreatment with bleaching earth ensures that the feedstock is purified, resulting in a high-quality final oleochemical product with minimal impurities and undesirable colors.
Spent bleaching earth, which contains absorbed impurities, is typically removed as sludge. It can be disposed of or processed further for material recovery or safe disposal.
Yes, the amount of bleaching earth used, and the pretreatment conditions can be adjusted based on the specific characteristics of the feedstock and the quality requirements of the final oleochemical product.
The filtration system should be cleaned or replaced regularly, depending on the level of contamination and the frequency of use. Regular maintenance ensures efficient operation and prevents processing delays.