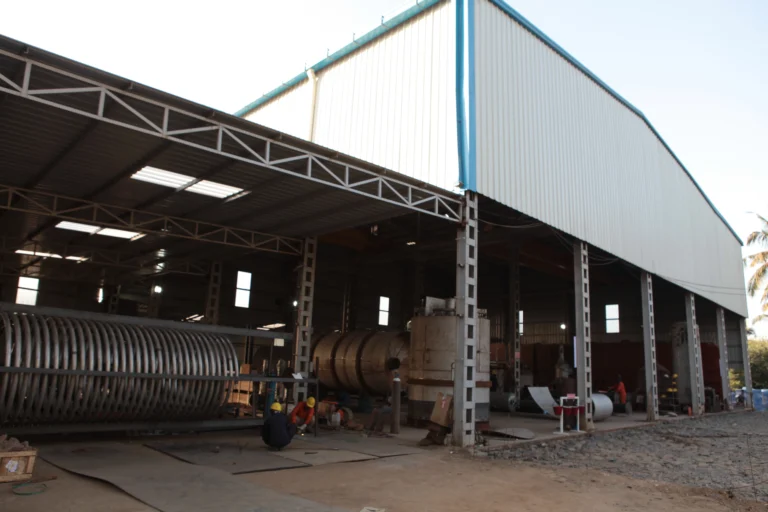
Miscella Distillation
Precision Distillation to Maximize Oil Purity and Minimize Losses.
Precision Distillation to Maximize Oil Purity and Minimize Losses.
Miscella distillation is a crucial step in the solvent extraction process of oils from seeds or other materials. It involves separating the solvent (usually hexane) from the oil-rich solution obtained after extraction.
The main purpose of miscella distillation is to recover the solvent used in the extraction process and to obtain a concentrated crude oil for further refining. It ensures that the extracted oil is free from solvent residues, making it safe for consumption or further processing.
1) The first step involves heating the solvent-oil mixture obtained from the extractor under reduced pressure in a distillation unit.
2) Hexane has a lower boiling point compared to the oil, so under controlled conditions, the hexane vaporizes and is separated from the oil.
3) The hexane vapor is condensed back into liquid form through cooling, collected, and recycled back into the extraction process to minimize solvent losses.

Strategies to ensure proactive domination. At the end of the day,User generated content in real-time will have multiple touchpoints for offshoring.























March 15, 2025
October 20, 2024
Discover some of the most asked questions regarding Miscella Distillation Plant.
Miscella distillation is the process of separating and recovering solvents (usually hexane) from the miscella, a mixture of oil and solvent obtained after extraction.
It is crucial for recovering valuable solvents for reuse, ensuring that the oil is free from residual solvents, and meeting regulatory and quality standards.
The process involves heating the miscella to evaporate the solvent, which is then condensed and recovered, while the oil remains in the distillation column.
Typical conditions include specific temperatures and pressures, depending on the solvent’s boiling point and the desired separation efficiency.
Key considerations include proper handling and recovery of solvents to minimize emissions, and ensuring that the process adheres to environmental regulations.
Quality is monitored through periodic sampling and testing to ensure that the residual solvent levels meet regulatory limits and the oil quality is maintained.